 Surprising Causes of Chest Pain
Surprising Causes of Chest PainAmazing causes of chest pain Attack This may feel like a heart attack. In addition to chest pain, you may be short of breath, feel your heart race, or become numb in your hands or feet. Some people feel dizzy or care that they're about to die. A stressful event can bring it, or it could get out of the blue. Panic attacks can be hard to handle on your own. They can get worse if you don't get help with them. Shingles If you have chest pain along with a painful rash and blisters on your chest or back, you may have this disease, which is caused by the chickenpox virus. If the nerves of the chest wall are affected, the pain can be severe. Stomach can be cleared on its own, but your doctor may give you medication to help with your symptoms or make it disappear faster. Hernia Under the lungs, there is a small area where the stomach and esophagus (your food pipe) are found. Toast, heavy lifting or tension during bowel movements can exert pressure on this area. If there is too much pressure, part of your stomach can be pushed into the opening. It's called hernia hial. Breast pain is a symptom, and it is also stomach pain or esophagus, swelling, itching and bitter taste at the back of the throat. Most hernias do not need treatment, but some people eventually need surgery. Gallstones These are hardened pieces of digestive fluid in the gallbladder. They can be as small as a grain of sand or as big as a golf ball. If you block the path between the gallbladder and bile ducts (which carry waste of your body), you can get a sudden pain in your stomach that also feels in your chest, back, or right shoulder. This is very likely to happen at night after a heavy meal. Heartburn If your stomach acids go up to your esophagus, you may feel pain not only in your chest, but also in your jaw and throat. Alcohol, smoking, aspirin and other non-inflammatory drugs, and citrus fruits can all be triggers. So you can eat too close to bedtime. Call your doctor if you don't feel better, or have other symptoms such as nausea or sweating. Muscle painThe most active or harder exercise than normal can strain the muscles on the chest wall. You may notice that your pain is worse when you are sitting or standing in a certain way. Breathing deep or pressing on the pained area could hurt. Step back into your training and do not lift heavy things until pain improves. A heating pad or ice pack in the area can help. Esophageal spasms are a common cause of chest pain, so consider your symptoms.. Syphilis This rare sexually transmitted disease (ETS) can cause problems with the lungs. Symptoms include a skin rash, fatigue, headache, and muscle pain. In some people, it also causes extra noise to accumulate around your lungs. This can cause acute chest pain and a cough with mucus. Antibiotics will help clear it up. AsmaChest stiffness is a symptom of this, along with cough, whipping and breathing struggle. It can be triggered by many different things, from dust and pet hair to certain things in food or physical activity. Medicines can help keep the airways open and help when symptoms occur. Pinched Nerve If you have pinched a nerve in your neck or collarbone, you may feel chest or back pain. Excessive pressure on the nerve can prevent it from working as it should. You could have a tingling sensation "pins and needles", and your skin could be very tender. This can usually be treated with relief from free selling pain and steroid shots. If that doesn't help, surgery may be needed to relieve pressure. Pulmonary Embolism This is when a blood clot forms somewhere in your body, then works your way to your lungs. Keep your lungs from getting enough blood. Your chest can hurt when you breathe deeply, cough, eat or fold. You may notice that the pain gets worse when you are active and does not improve when you stop. If this happens, get medical help right away. Medicine can prevent clot from becoming larger and prevent further formation. Spleen Block This organ lives behind its left rib and helps protect your body from infection. It is rare, but blood flow to your spleen can be blocked due to a blood clot, infection, or disease. If that happens, the tissue there can start to die. This is called splenic infarction. Some people have no symptoms, but others have chest pain, often on the left side. It can improve with medication but it can become serious if it is not treated. AnginaIf your body does not send enough blood to your heart, you will feel a pressure that squeezes you in your chest. That's called angina. Some people also feel pain in their shoulders, arms, neck, jaw and back. It can be triggered by stress, heavy meals or exercise. Or it could be a sign of another heart problem. You are more likely to have it if your cholesterol or blood pressure is high, has diabetes or does not exert or eat healthy foods. Pleurisy If taking a deep breath, coughing or sneezing brings chest pain, the lining of the lungs can be inflated. Pleurisy called, this can be caused by a virus, bacterial infection, or certain medications you take. Many liquids and ibuprofen for free sale, such as Advil or Motrin, can help. But if you also have fever or pain lasts longer than a few days, consult your doctor. Costocondritis This is when tissue in the rib cage is inflamed due to arthritis, injury or infection. You may feel a severe pain, pain or pressure on your sides. It could get worse after working or moving the torso a lot. There's no cure, and it can last up to a year. Acetaminophen of free sale (Tylenol) or ibuprofen can help. A hot compress or heating pad at the pain site will give relief, too. Heart Attack The chest pain is the most common symptom of heart attack. If you feel crushing pressure that lasts longer than a few minutes, nausea, severe breathing difficulty, or chest pain or left upper arm, call 911. Women who are having a heart attack may have more subtle symptoms. Along with chest pain, you may feel tired, have back or jaw pain, or feel dizzy. All these are signs that you need an ambulance right away. Next Slideshow Title1 Reviewed by IMAGES PROVIDED BY:1) PeopleImages / Getty Images2) clsgraphics /iStockPhoto3) Gwen Shockey / Science Source4) Springer Medizin / Science Source5) cyano66 / Thinkstock6) Brainsil / Thinkstock7) royaltystockphoto / Thinkstock8 IAN HOOTON/SPL / Getty Images9) Mayo Clinic: "The chest pain", "Gallstones", "Pleurisy", "Attacks of panic and panic disorder", "Angina", "Costocronditis", "Costocronditis" National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Insecticid Diseases: "The Gas Calculations." CDC: "Shingles (Herpes Zoster)," "Syphilis -- CDC Fact Sheet." Elzouki, A., Al-Kawaaz, M., et al., "Case Reports in Infectious Diseases", Volume 2012.UpToDate: "Cest Pain (Beyond the Basics)". The NHS chooses: "The chest pain".On the health of children: "The chest pain", the spleen and the lymph system."MedScape: "Splenic Infarct."Koyuncu, M., Kostekci, S., et al. "Eurasian Journal of Emergency Medicine", 4/21/15. Weill Cornell Brain and Spine Center: "Radiculopathy." Washington University in St. Louis: "Torachic Outlet Syndrome". Yazici, P., Kaya, C., et al. "International Journal of Surgery Case Reports", Vol. 10, 2015. David, G., Perpoint, T., et al. "Infectious chronic diseases", 2006, 42 (3). Cleveland Clinic: "Hiatal Hernia". Instituto Nacional de Corazón, Pulmón y Sangre: "What are the signs and symptoms of asthma?" How is Asma treated and controlled? This tool does not provide medical advice. This work does not prohibit medical help. It is intended for general information purposes only and does not address individual circumstances. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment and should not be based on making decisions about your health. Never ignore the professional medical advice in the search for treatment due to something you have read on the WebMD site. If you think you may have a medical emergency, call your doctor immediately or call 911. WebMD Slideshows See our presentations to learn more about your health. Top PicksHealth SolutionsMore WebMD Policies About WebMD Network Our applications for advertisers © 2005 - 2021 WebMD LLC. All rights reserved. DMA does not provide medical advice, diagnosis or treatment.
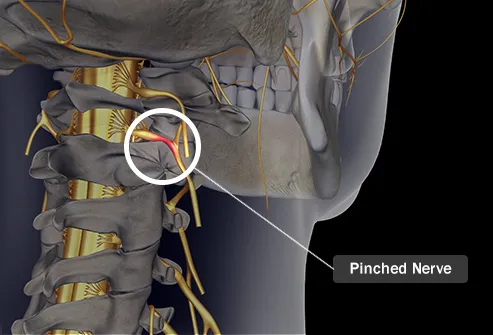
Cleveland Clinic Menu Pinched Nerves Overview What is a pinched nerve? A pinched nerve is a compressed nerve. The tissues surrounding the nerve roots can cause pain, numbness and tingling in different areas of the body. In many cases, the cause is a slip between the vertebrae in the spinal cord and press the spinal nerve down the leg. Most pinched nerves originate in the neck (cervical spinal disease), the upper part of the middle back (thoracic spinapathy) or the lower part of the back (lumbar spinapathy). You can also experience pinched nerves in the hand, elbow and wrist (for the wrist). Pricked nerves can affect several areas of your body: A pinched nerve can be painful, but it is usually treatable with rest, free-sale medication and physical therapy. Most people recover completely from a pinched nerve. How common is a pinched nerve? Pricked nerves are common; every year around 85 out of 100,000 adults in the United States are affected by pinched nerves. People of any age may experience pinched nerves, but those over 50 years are more likely to have them, due to arthritis and degeneration in the spine and other parts of the body. Where are the pinched nerves in my body? Pricked nerves can occur throughout the body based on the location of the affected nerves. The most common areas in which you will feel the effects of a pinched nerve are: Will it be a pinched nerve disappear on its own? How long does it take? Yes, most over time (usually four to six weeks). You can improve symptoms with rest and pain medications such as naproxen, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen. If the home treatment does not provide relief after several days, call your provider, which will give you more guidance. You may be asked to come to the office for evaluation and evidence. Can a pinch nerve lead to more serious problems? A pinched nerve can become serious, causing chronic pain, or even causing permanent nerve damage. Fluid and swelling can cause irreversible damage to the nerves, so make sure you contact your provider if your symptoms get worse or don't get better after several days. Symptoms and Causes What causes a pinched nerve? Some conditions may cause tissue or bone to compress a nerve and cause symptoms. These include: What are the symptoms of a pinched nerve? Diagnosis and Tests How is a pinch nerve diagnosed? You will want to visit a healthcare provider about your pinched nerve if you do not respond to home conservative treatment. To find the source of the pinched nerve, suppliers physically examine their neck, arms, shoulders and wrist and hands. They will seek muscle weakness, test changes in reflexes and ask about the different sensations they feel. Image tests If necessary, you may be asked to submit to one or more of these procedures to track the source of the problem: Management and treatment How is a pinched nerve treated? The medical (non-surgical) administration is the first line of treatment for pinched nerves. This includes: Surgery Surgery is the last resort to treat a pinched nerve when non-surgical treatment has not relieved pressure on nerves. Examples of surgeries that fix the compression of the spinal nerve include: After these surgeries, a complete recovery of strength and movement may take several months. Most people can return to a work desk within a few days to a few weeks after surgery. Depending on the surgery, return to full activities may take three to four months. Your surgeon will give you a general idea of your recovery time, and some people may take longer. Prevention How can I prevent a pinched nerve? Not all pinched nerves can be prevented, but you can lower your risk if: Perspectives / Prognosis What is the prospect of a pinched nerve? Many people recover completely from a pinched nerve with home treatment. When medical or surgical treatment is needed, the prospect for full recovery is excellent. Living with When should I see my healthcare provider about a pinched nerve? If the pain and other symptoms of your pinched nerve have not shown any signs of relief after several days, call your provider. Last reviewed by a medical professional from Cleveland Clinic on 04/07/2020. References Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not support products or services of Clinics no Cniles. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not support products or services of Clinics no Cniles. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not support products or services of Clinics no Cniles. Institutes and Related Services Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not support products or services of Clinics no Cniles. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not support products or services of Clinics no Cniles. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not support products or services of Clinics no Cniles. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not support products or services of Clinics no Cniles. Cleveland Clinic is a non-profit academic medical center. Advertising on our site helps support our mission. We do not support products or services of Clinics no Cniles. More health news + info
Treatment of Pinched Nerve in the Neck in NJ | Pain Management Doctor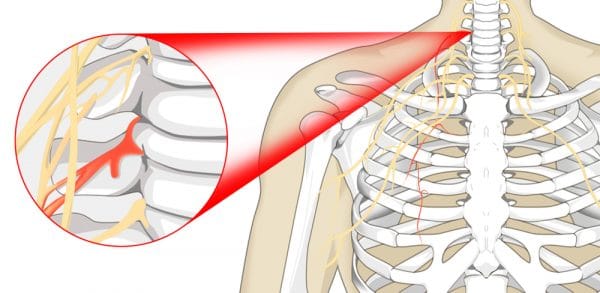
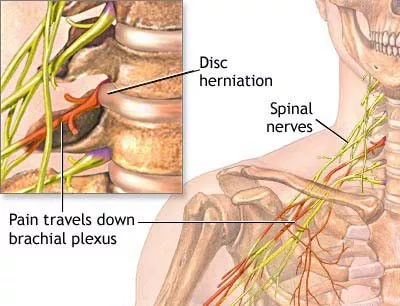
Pinched Nerve causes, symptoms & treatment | Zaker Chiro:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pinched-nerve-headache-treatment-1719581-5c04ae4146e0fb0001cc1846-63608779dc594598ae4331423b0d2aed.png)
Pinched Nerve: Overview and More
Sciatica & Pinched Nerve Pain: Symptoms, Causes & Lower Back Treatment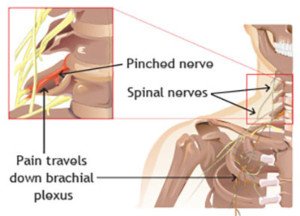
Shoulder Pain from Heart Attack vs. Pinched Nerve in Neck » Scary Symptoms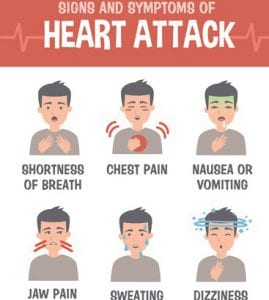
Chest Pain: Is it a Heart Attack or Your Spine? - Physio Works...
Can cervical spine instability cause heart palpitations and blood pressure problems? – Caring Medical Florida
Pinched Nerve in Neck Causes, Symptoms & Treatments
Heterotopic Pain | Ensoma Body Works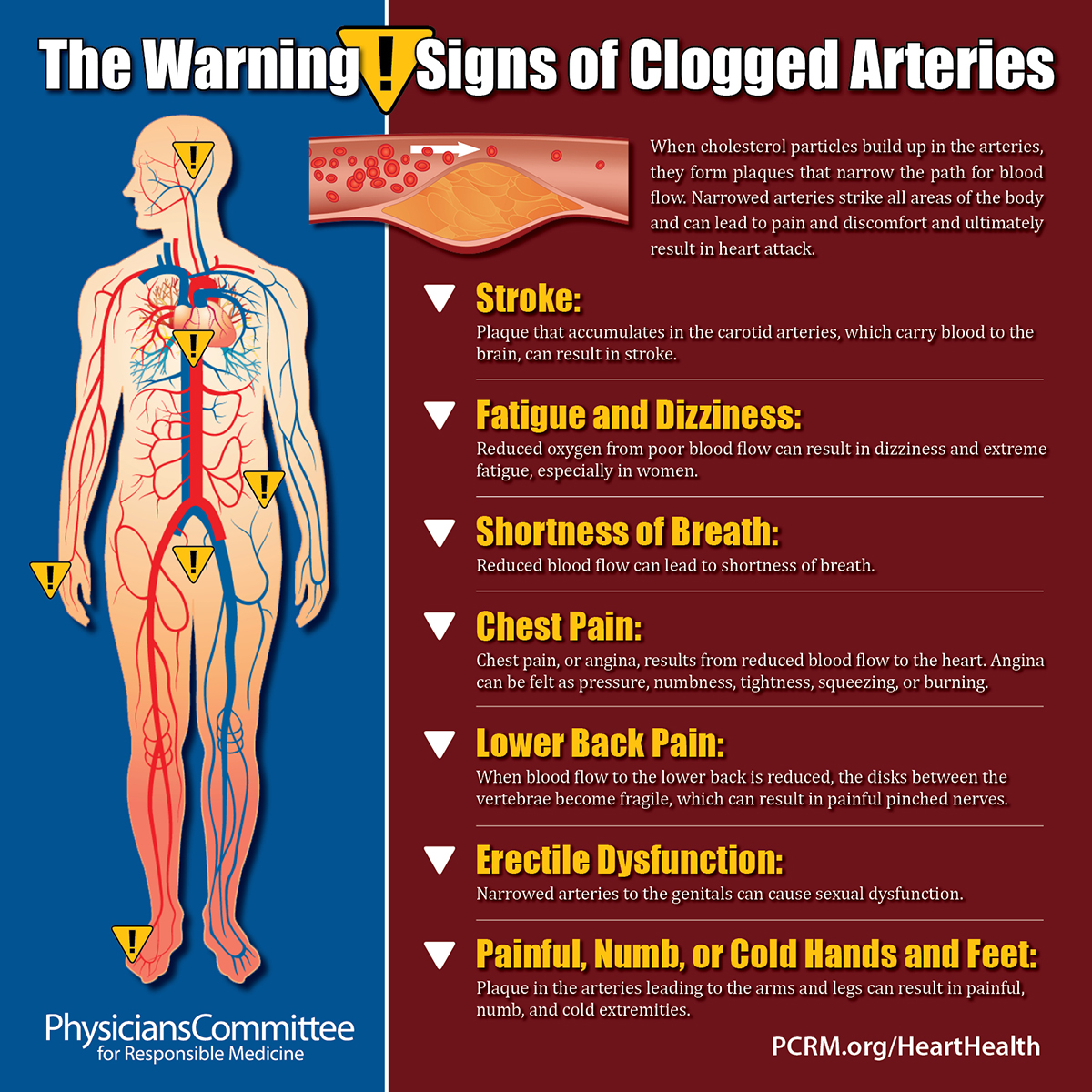
The Warning Signs of Clogged Arteries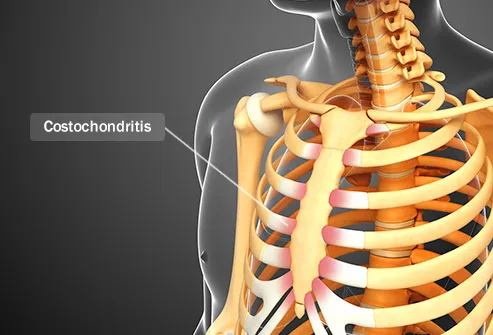
Surprising Causes of Chest Pain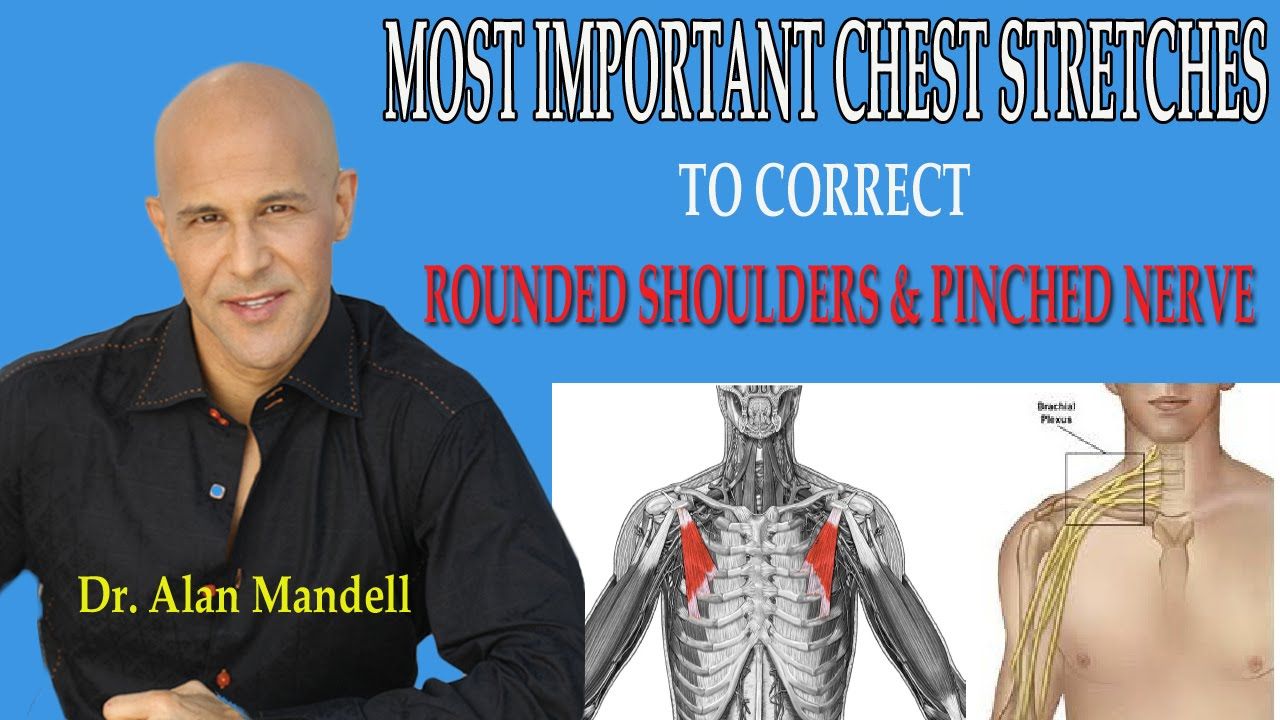
Most Important Chest Stretches to Correct Forward Rounded Shoulders and Pinched Nerve - Dr Mandell | Pinched nerve, Nerve doctor, Muscle stretches
Pinched Nerve in Neck: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatments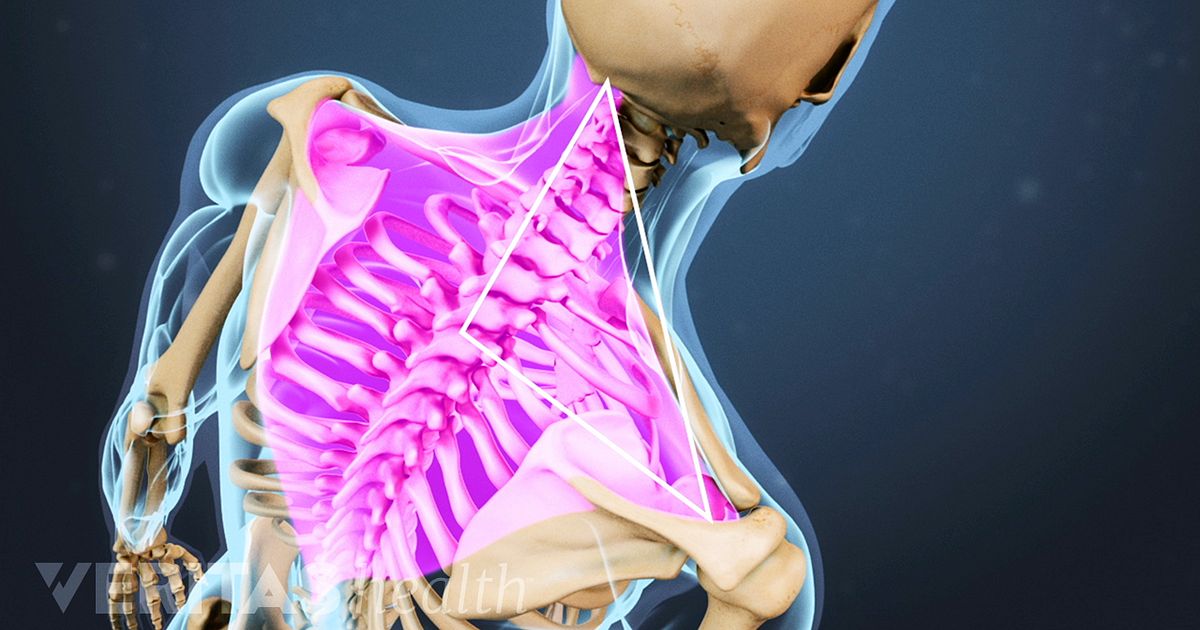
Understanding Upper Back and Chest Pain
Pinched Nerve Information | Florida Orthopaedic Institute
Chest Pain: 33 Causes, Symptoms, Signs, COVID-19 & Types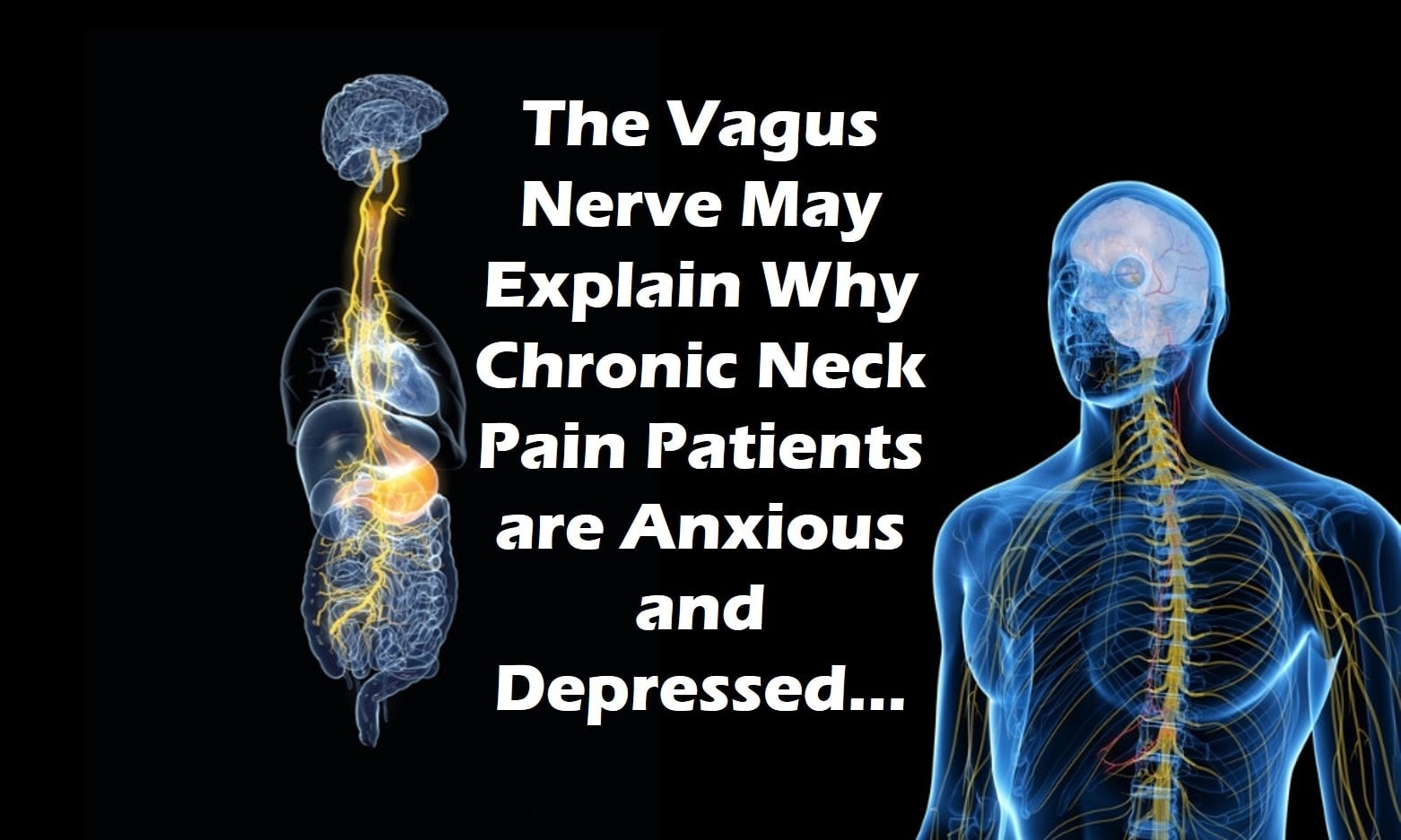
The Vagus Nerve, Neck Pain, Headaches, and Anxiety | Regenexx Blog
Can cervical spine instability cause heart palpitations and blood pressure problems? – Caring Medical Florida
Pinched Nerves Can Cause Back and Neck Pain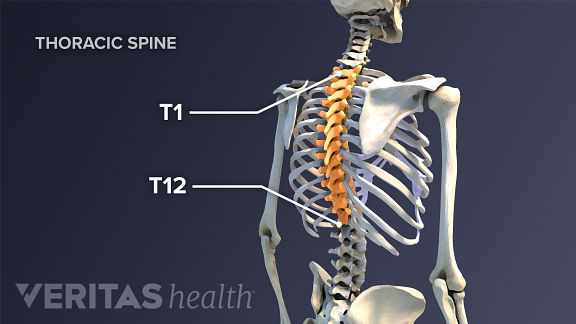
Understanding Upper Back and Chest Pain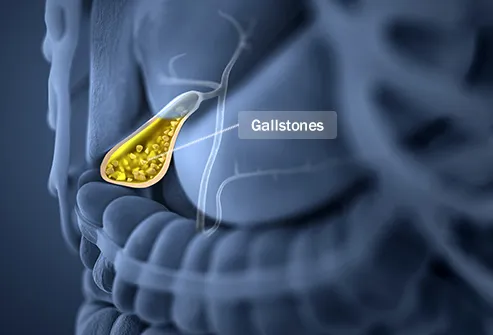
Surprising Causes of Chest Pain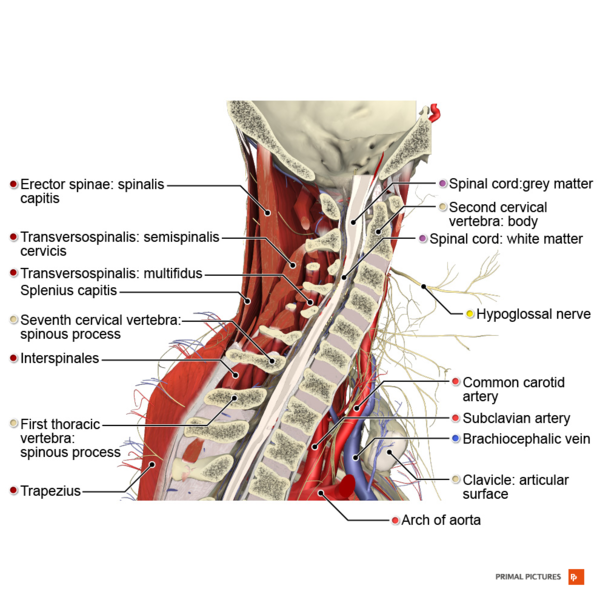
Cervical Radiculopathy - Physiopedia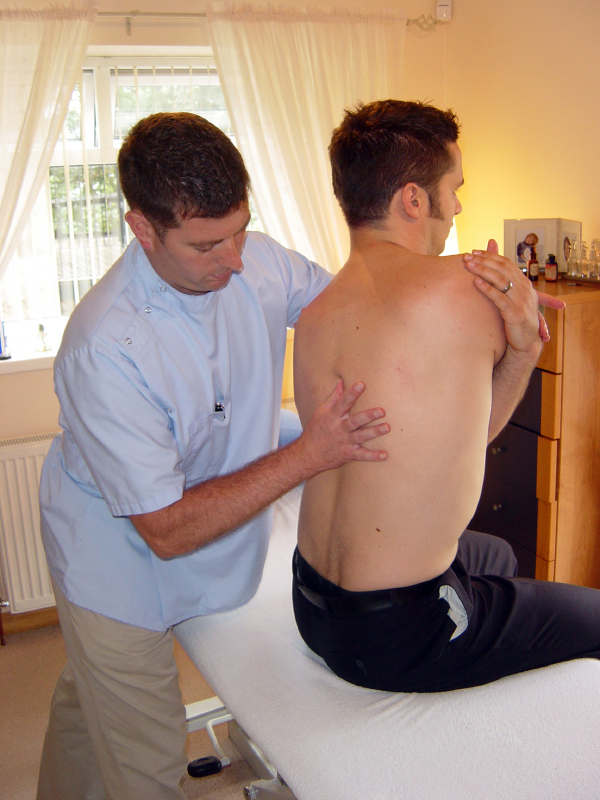
Can a Pinched Nerve Cause Chest Pain? If So, How Does This Happen?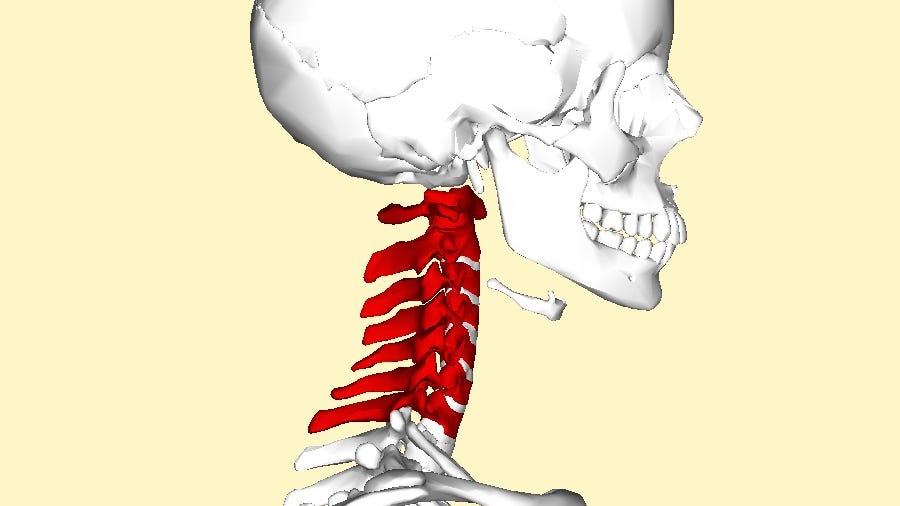
Pinched nerve pain can radiate to other areas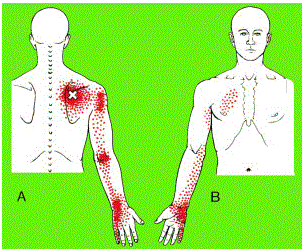
A Cervical Radiculopathy Can Cause Chest Pain - ACR Meeting Abstracts
Pinched Nerve in the Upper Back: Causes, Treatments, and More
Pin on health and beauty
Chest and Shoulder Pain: Symptoms, Causes, and Diagnosis:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/right-sided-chest-pain-symptoms-and-possible-causes-4116859-5c77334ec9e77c00012f815f.png)
Causes of Right Side Chest Pain
Pin on Symptoms
5 Signs of a Pinched Nerve | SELF
Chest Pain: 33 Causes, Symptoms, Signs, COVID-19 & Types
Referred Pain Around The Shoulder - Everything You Need To Know - Dr. Nabil Ebraheim - YouTube
Pinched Nerve in Neck, Back, Shoulder & More: Symptoms, Treatments, Causes
Can a Chiropractor Help Your Pinched Nerve?
Is a Pinched Nerve Causing the Numbness and Tingling in Your Hands? - Dr. Dean Collins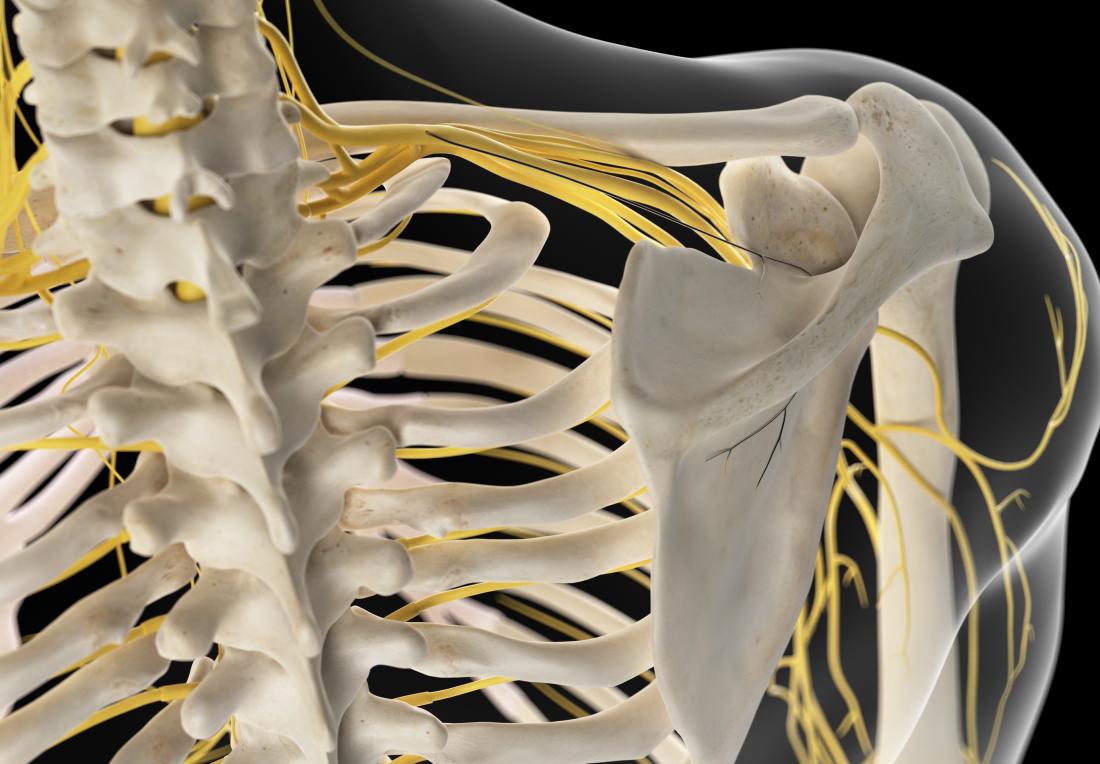
Pain in right side of neck: 9 causes
Pinched Nerves Can Cause Back and Neck Pain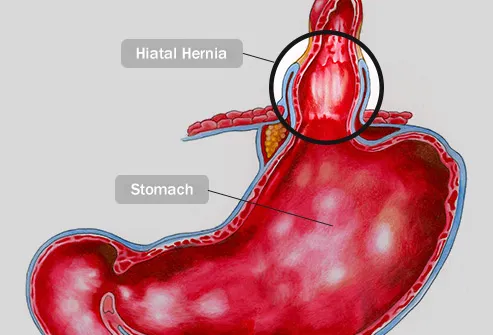
Surprising Causes of Chest Pain
pinched nerve in neck
 Surprising Causes of Chest Pain
Surprising Causes of Chest Pain

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/pinched-nerve-headache-treatment-1719581-5c04ae4146e0fb0001cc1846-63608779dc594598ae4331423b0d2aed.png)

























:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/right-sided-chest-pain-symptoms-and-possible-causes-4116859-5c77334ec9e77c00012f815f.png)










Posting Komentar untuk "can a pinched nerve in neck cause chest pain"